Visa policy of Guinea
Politics of Guinea |
|---|
 |
| Constitution
|
| Government
|
| Parliament
|
|
| Elections
|
| |
|
Visitors to Guinea must obtain an eVisa unless they come from one of the countries or territories that are visa exempt. Alternatively visas can be obtained from a Guinean diplomatic mission. [1]
Visa policy map
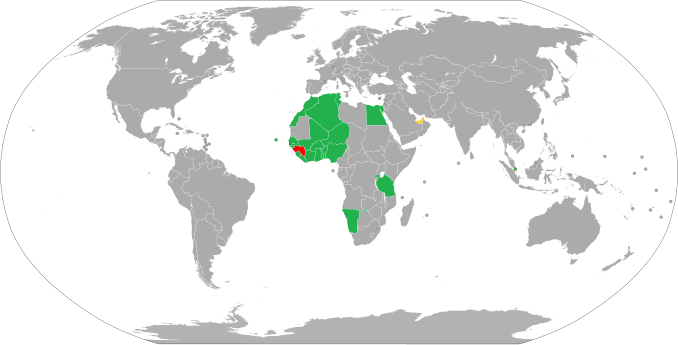
Visa exemption
Citizens of the following 21 countries as well as refugees and stateless persons residing in these countries can visit Guinea without a visa:[1][2]
In addition, according to Timatic, nationals of China holding ordinary passports endorsed "for public affairs" do not require a visa for a maximum stay of 30 days.[1]
| Date of visa changes | |
|---|---|
Visa free
Visa on arrival
|
Non-ordinary passports
Additionally, holders of diplomatic or service passports issued to nationals of China, Romania, Russia, South Africa[6] and Zimbabwe do not require a visa for a maximum stay of 90 days. Holders of diplomatic passports of Turkey do not require a visa for a stay of up to 90 days.
Visa on arrival
According to Timatic, nationals of the United Arab Emirates can obtain a visa on arrival for a maximum stay of 90 days.[1] This information, however, is not supported by the official website of the Central Directorate of the Border Police (DCPAF) of the Ministry of Security and Civil Protection of Guinea, which states that UAE nationals must obtain an eVisa.[2]
Electronic Visa (e-Visa)
Nationals of all countries and territories that require a visa can obtain an electronic visa.[2] E-Visa is available for stay up to 90 days.[2]
Citizens of Canada and the United States who obtain an e-Visa can stay in Guinea for up to 5 years.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "Visa and passport". Timatic. International Air Transport Association through Emirates. Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Guinea Visa". www.paf.gov.gn. Ministry of Security and Civil Protection - Government of Guinea. 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ "Treaty Establishing the Economic Community of West African States - Protocol A/P1/5/79 on Free Movement of Persons, Right of Residence and Establishment". Archived from the original on 14 June 2018 – via United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
- ^ "新·头条|几内亚给予新加坡护照免签待遇 世界最强大护照190目的地免签 - 华人头条". www.52hrtt.com (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 1 November 2019. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ "Emiratis get visa on arrival for west African country". 19 April 2018.
- ^ Under visa exemption agreement on 24 November 2006; from 23 January 2007 [1]































