3 Monocerotis
  | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Monoceros |
| Right ascension | 06h 01m 50.42241s[1] |
| Declination | −10° 35′ 52.5565″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.92[2] (4.98 + 8.25)[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B5 III[4] |
| U−B color index | −0.58[5] |
| B−V color index | −0.12[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +39.00[6] km/s |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.94[2] |
| A | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −8.282[7] mas/yr Dec.: 4.385[7] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.5717 ± 0.3115 mas[7] |
| Distance | 710 ± 50 ly (220 ± 10 pc) |
| B | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 6.990[8] mas/yr Dec.: 4.574[8] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.1006 ± 0.0960 mas[8] |
| Distance | 1,050 ± 30 ly (323 ± 10 pc) |
| Details | |
| 3 Mon A | |
| Mass | 5.85[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.5[10] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,105[2] L☉ |
| Temperature | 15,000[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.00[11] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 45[12] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
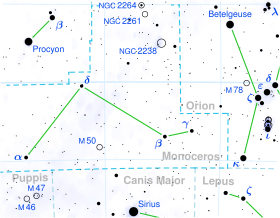
3 Monocerotis is a binary star[3] system in the equatorial constellation of Monoceros, located approximately 780 light years away from the Sun based on parallax.[1] It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.92.[2] The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +39 km/s.[6]
The magnitude 4.98 primary, designated component A, has a stellar classification of B5 III,[4] matching an evolved blue giant star. It has 5.85[9] times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 1,105[2] times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 15,000 K.[9] The companion, component B, is magnitude 7.96 with an angular separation of 1.9″ from the primary.[14]
References
- ^ a b c Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ a b c d e Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ a b Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, S2CID 14878976.
- ^ a b Hoffleit, D.; Warren, W. H. (1995). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Hoffleit+, 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: V/50. Originally Published in: 1964BS....C......0H. 5050. Bibcode:1995yCat.5050....0H.
- ^ a b Mallama, A. (2014). "Sloan Magnitudes for the Brightest Stars". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers. 42 (2): 443. Bibcode:2014JAVSO..42..443M.Vizier catalog entry
- ^ a b Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b c Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d Hohle, M.M.; Neuhäuser, R.; Schutz, B.F. (2010). "Masses and luminosities of O- and B-type stars and red supergiants". Astronomische Nachrichten. 331 (4): 349. arXiv:1003.2335. Bibcode:2010AN....331..349H. doi:10.1002/asna.200911355. S2CID 111387483. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ Pasinetti Fracassini, L. E.; et al. (February 2001). "Catalogue of Apparent Diameters and Absolute Radii of Stars (CADARS)". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 367 (2) (Third ed.): 521–524. arXiv:astro-ph/0012289. Bibcode:2001A&A...367..521P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000451. S2CID 425754.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2012). "Dependence of kinematics on the age of stars in the solar neighborhood". Astronomy Letters. 38 (12): 771–782. arXiv:1606.08814. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..771G. doi:10.1134/S1063773712120031. S2CID 118345778. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ Abt, Helmut A.; Levato, Hugo; Grosso, Monica (2002). "Rotational Velocities of B Stars". The Astrophysical Journal. 573 (1): 359–365. Bibcode:2002ApJ...573..359A. doi:10.1086/340590.
- ^ "3 Mon". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- ^ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal. 122 (6): 3466. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M. doi:10.1086/323920. Vizier catalog entry
- v
- t
- e
| Bayer | |
|---|---|
| Flamsteed | |
| Variable | |
| HR |
|
| HD | |
| Other |
| Exoplanets |
|---|
clusters
| NGC | |
|---|---|
| Other |
| NGC | |
|---|---|
| Other |
| NGC |
|---|
 Category
Category









