INHBA
| INHBA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | INHBA, EDF, FRP, inhibin beta A, inhibin beta A subunit, inhibin subunit beta A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 147290 MGI: 96570 HomoloGene: 1653 GeneCards: INHBA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Inhibin, beta A, also known as INHBA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the INHBA gene.[5] INHBA is a subunit of both activin and inhibin, two closely related glycoproteins with opposing biological effects.
Function
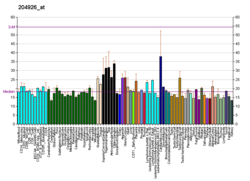
The inhibin beta A subunit joins the alpha subunit to form a pituitary FSH secretion inhibitor. Inhibin has been shown to regulate gonadal stromal cell proliferation negatively and to have tumor-suppressor activity. In addition, serum levels of inhibin have been shown to reflect the size of granulosa-cell tumors and can therefore be used as a marker for primary as well as recurrent disease. Because expression in gonadal and various extragonadal tissues may vary several fold in a tissue-specific fashion, it is proposed that inhibin may be both a growth/differentiation factor and a hormone. Furthermore, the beta A subunit forms a homodimer, activin A, and also joins with a beta B subunit to form a heterodimer, activin AB, both of which stimulate FSH secretion. Finally, it has been shown that the beta A subunit mRNA is identical to the erythroid differentiation factor subunit mRNA and that only one gene for this mRNA exists in the human genome.[6]
Interactions
INHBA has been shown to interact with ACVR2A.[7][8]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000122641 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000041324 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Burger HG, Igarashi M (April 1988). "Inhibin: definition and nomenclature, including related substances". Endocrinology. 122 (4): 1701–2. doi:10.1210/endo-122-4-1701. PMID 3345731.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: INHBA inhibin, beta A (activin A, activin AB alpha polypeptide)".
- ^ Lewis KA, Gray P C, Blount A L, MacConell L A, Wiater E, Bilezikjian L M, Vale W (March 2000). "Betaglycan binds inhibin and can mediate functional antagonism of activin signalling". Nature. 404 (6776). ENGLAND: 411–4. Bibcode:2000Natur.404..411L. doi:10.1038/35006129. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 10746731. S2CID 4393629.
- ^ Martens JW, de Winter J P, Timmerman M A, McLuskey A, van Schaik R H, Themmen A P, de Jong F H (July 1997). "Inhibin interferes with activin signaling at the level of the activin receptor complex in Chinese hamster ovary cells" (PDF). Endocrinology. 138 (7). UNITED STATES: 2928–36. doi:10.1210/endo.138.7.5250. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 9202237.
Further reading
- Munz B, Hübner G, Tretter Y, et al. (1999). "A novel role of activin in inflammation and repair". J. Endocrinol. 161 (2): 187–93. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1610187. PMID 10320815.
- Welt C, Sidis Y, Keutmann H, Schneyer A (2002). "Activins, inhibins, and follistatins: from endocrinology to signaling. A paradigm for the new millennium". Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood). 227 (9): 724–52. doi:10.1177/153537020222700905. PMID 12324653. S2CID 19795772.
- Shav-Tal Y, Zipori D (2003). "The role of activin a in regulation of hemopoiesis". Stem Cells. 20 (6): 493–500. doi:10.1634/stemcells.20-6-493. PMID 12456957. S2CID 36242096.
- Reis FM, Luisi S, Carneiro MM, et al. (2005). "Activin, inhibin and the human breast". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 225 (1–2): 77–82. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2004.02.016. PMID 15451571. S2CID 24201803.
- Shao L, Frigon NL, Young AL, et al. (1992). "Effect of activin A on globin gene expression in purified human erythroid progenitors". Blood. 79 (3): 773–81. doi:10.1182/blood.V79.3.773.bloodjournal793773. PMID 1310063.
- Mathews LS, Vale WW (1991). "Expression cloning of an activin receptor, a predicted transmembrane serine kinase". Cell. 65 (6): 973–82. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90549-E. PMID 1646080. S2CID 36407277.
- Tanimoto K, Handa S, Ueno N, et al. (1992). "Structure and sequence analysis of the human activin beta A subunit gene". DNA Seq. 2 (2): 103–10. doi:10.3109/10425179109039678. PMID 1777673.
- Mason AJ, Berkemeier LM, Schmelzer CH, Schwall RH (1990). "Activin B: precursor sequences, genomic structure and in vitro activities". Mol. Endocrinol. 3 (9): 1352–8. doi:10.1210/mend-3-9-1352. PMID 2575216.
- Barton DE, Yang-Feng TL, Mason AJ, et al. (1989). "Mapping of genes for inhibin subunits alpha, beta A, and beta B on human and mouse chromosomes and studies of jsd mice". Genomics. 5 (1): 91–9. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(89)90091-8. PMID 2767687.
- Murata M, Eto Y, Shibai H, et al. (1988). "Erythroid differentiation factor is encoded by the same mRNA as that of the inhibin beta A chain". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (8): 2434–8. Bibcode:1988PNAS...85.2434M. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.8.2434. PMC 280011. PMID 3267209.
- Burger HG, Igarashi M (1988). "Inhibin: definition and nomenclature, including related substances". Endocrinology. 122 (4): 1701–2. doi:10.1210/endo-122-4-1701. PMID 3345731.
- Mason AJ, Niall HD, Seeburg PH (1986). "Structure of two human ovarian inhibins". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135 (3): 957–64. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(86)91021-1. PMID 3754442.
- Stewart AG, Milborrow HM, Ring JM, et al. (1986). "Human inhibin genes. Genomic characterisation and sequencing". FEBS Lett. 206 (2): 329–34. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(86)81006-7. PMID 3758355. S2CID 21261385.
- Sumitomo S, Inouye S, Liu XJ, et al. (1995). "The heparin binding site of follistatin is involved in its interaction with activin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 208 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1297. PMID 7887917.
- Xu J, McKeehan K, Matsuzaki K, McKeehan WL (1995). "Inhibin antagonizes inhibition of liver cell growth by activin by a dominant-negative mechanism". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (11): 6308–6313. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.11.6308. PMID 7890768.
- Mason AJ (1994). "Functional analysis of the cysteine residues of activin A". Mol. Endocrinol. 8 (3): 325–32. doi:10.1210/mend.8.3.8015550. PMID 8015550. S2CID 7615672.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Nishihara T, Okahashi N, Ueda N (1994). "Activin A induces apoptotic cell death". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197 (2): 985–91. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1993.2576. PMID 8267637.
- ten Dijke P, Ichijo H, Franzén P, et al. (1993). "Activin receptor-like kinases: a novel subclass of cell-surface receptors with predicted serine/threonine kinase activity". Oncogene. 8 (10): 2879–87. PMID 8397373.
- Tanimoto K, Yoshida E, Mita S, et al. (1997). "Human activin betaA gene. Identification of novel 5' exon, functional promoter, and enhancers". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (51): 32760–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.51.32760. PMID 8955111.
- v
- t
- e
| ALK1 (ACVRL1) | |
|---|---|
| ALK2 (ACVR1A) | |
| ALK3 (BMPR1A) | |
| ALK4 (ACVR1B) | |
| ALK5 (TGFβR1) |
|
| ALK6 (BMPR1B) | |
| ALK7 (ACVR1C) |
| TGFβR2 |
|
|---|---|
| BMPR2 | |
| ACVR2A (ACVR2) | |
| ACVR2B | |
| AMHR2 (AMHR) |
|
| TGFβR3 (β-glycan) |
|---|
- Endogenous antagonists/inhibitors: BAMBI
- Cerberus (CER1)
- Chordin
- DAN (PARN)
- Decorin
- Follistatin
- Gremlin (Drm)
- LTBP1
- Noggin
- TGIF
- Thrombospondin 1 (THBS1)
- Tomoregulin 1
- Antibodies: Stamulumab (against myostatin)
- TRC105 (against endoglin)
- Others: Endoglin