Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.161 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C10H10BFeF4 |
| Molar mass | 272.84 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark blue powder |
| Melting point | 178 °C (352 °F; 451 K) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in acetonitrile | Soluble[citation needed] |
| Hazards[1] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
Pictograms |  |
| Danger | |
Hazard statements | H314 |
Precautionary statements | P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | Ferrocene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
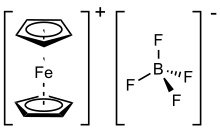
Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate is an organometallic compound with the formula [Fe(C5H5)2]BF4. This salt is composed of the cation [Fe(C5H5)2]+ and the tetrafluoroborate anion (BF−
4). The related hexafluorophosphate is also a popular reagent with similar properties. The ferrocenium cation is often abbreviated Fc+ or Cp2Fe+. The salt is deep blue in color and paramagnetic. Ferrocenium salts are sometimes used as one-electron oxidizing agents, and the reduced product, ferrocene, is inert and readily separated from ionic products. The ferrocene–ferrocenium couple is often used as a reference in electrochemistry. The standard potential of ferrocene-ferrocenium is dependent on specific electrochemical conditions.[2]
Preparation
Commercially available, this compound may be prepared by oxidizing ferrocene typically with ferric salts followed by addition of fluoroboric acid.[2] A variety of other oxidants work well also, such as nitrosyl tetrafluoroborate.[3] Many analogous ferrocenium salts are known.[4]
Structure
According to X-ray crystallography, the structures of the metallocene component of FcBF4 and the parent ferrocene are very similar. The Fe-C distances in the cation are 209.5 pm, about 2% longer than the Fe-C distances in ferrocene. [5]
References
- ^ "Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate 482358". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ a b Connelly, N. G.; Geiger, W. E. (1996). "Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic Chemistry". Chemical Reviews. 96 (2): 877–910. doi:10.1021/cr940053x. PMID 11848774.
- ^ Nielson, Roger M.; McManis, George E.; Safford, Lance K.; Weaver, Michael J. (1989). "Solvent and electrolyte effects on the kinetics of ferrocenium-ferrocene self-exchange. A reevaluation". J. Phys. Chem. 93 (5): 2152. doi:10.1021/j100342a086.
- ^ Le Bras, J.; Jiao, H.; Meyer, W. E.; Hampel, F.; Gladysz, J. A. (2000). "Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Reactions of the 17-Valence-Electron Rhenium Methyl Complex [(η5-C5Me5)Re(NO)(P(4-C6H4CH3)3)(CH3)]+ B(3,5-C
6H
3(CF
3)
2)−
4: Experimental and Computational Bonding Comparisons with 18-Electron Methyl and Methylidene Complexes". J. Organomet. Chem. 616: 54–66. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)00531-3. - ^ Scholz, Stefan; Scheibitz, Matthias; Schödel, Frauke; Bolte, Michael; Wagner, Matthias; Lerner, Hans-Wolfram (2007). "Difference in Reactivity of Triel Halides EX3 Towards Ferrocene". Inorganica Chimica Acta. 360 (10): 3323–3329. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2007.03.049.
- v
- t
- e
- H2Fe(CO)4
- Na2Fe(CO)4
- Fe(CO)5
- Fe2(CO)9
- Fe3(CO)12
- Fe(CO)3CH3COC2H2C6H6
- FeH
| Organoiron(I) compounds |
|---|
- Fe3C
- FeH2
- Mg2FeH6
- FeF2
- FeCl2
- Fe(ClO4)2
- FeBr2
- FeI2
- FeO
- Fe(OH)2
- FeS
- FeSO4
- (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O
- FeSe
- FeSeO4
- Fe(NO3)2
- Fe3(PO4)2
- FeSi2
- Fe(BF4)2
- FeCr2O4
- FeMoO4
- FeTiO3
- FeCO3
- FeC2O4
- Fe(C2H3O2)2
- Fe(C3H5O3)2
- FeC6H6O7
- FeC12H22O14
- FeI2(CO)4
| Organoiron(II) compounds |
|
|---|
- Fe3O4
- Fe3S4
| Organoiron(III) compounds |
|
|---|
- FeF4
- K2FeO4
- BaFeO4










