| ATP13A2 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ATP13A2, CLN12, HSA9947, KRPPD, PARK9, ATPase 13A2, SPG78, ATPase cation transporting 13A2 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 610513; MGI: 1922022; HomoloGene: 56940; GeneCards: ATP13A2; OMA:ATP13A2 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1p36.13 | Start | 16,985,958 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 17,011,928 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 4 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 4|4 D3 | Start | 140,714,184 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 140,734,641 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - right frontal lobe
- right hemisphere of cerebellum
- prefrontal cortex
- anterior cingulate cortex
- pons
- Brodmann area 9
- anterior pituitary
- amygdala
- hypothalamus
- nucleus accumbens
|
| | Top expressed in | - external carotid artery
- internal carotid artery
- stroma of bone marrow
- dorsal tegmental nucleus
- perirhinal cortex
- neural layer of retina
- motor neuron
- entorhinal cortex
- superior colliculus
- superior frontal gyrus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 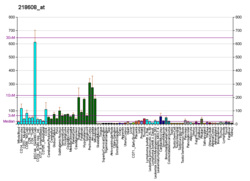 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - nucleotide binding
- metal ion binding
- ATPase activity
- protein binding
- hydrolase activity
- ATP binding
- cupric ion binding
- phosphatidic acid binding
- zinc ion binding
- phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding
- manganese ion binding
- P-type calcium transporter activity
- ATPase-coupled cation transmembrane transporter activity
| | Cellular component | - integral component of membrane
- membrane
- vesicle membrane
- integral component of plasma membrane
- transport vesicle
- lysosomal lumen
- lysosome
- vesicle
- multivesicular body
- neuron projection
- integral component of lysosomal membrane
- multivesicular body membrane
- autophagosome
- late endosome
- neuronal cell body
- lysosomal membrane
| | Biological process | - cellular cation homeostasis
- cation transport
- ion transmembrane transport
- regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion
- regulation of autophagosome size
- regulation of endopeptidase activity
- regulation of mitochondrion organization
- cellular response to oxidative stress
- cellular calcium ion homeostasis
- cellular response to manganese ion
- cellular iron ion homeostasis
- protein autophosphorylation
- cellular zinc ion homeostasis
- autophagosome organization
- regulation of glucosylceramidase activity
- regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy
- negative regulation of neuron death
- zinc ion homeostasis
- regulation of macroautophagy
- regulation of intracellular protein transport
- positive regulation of protein secretion
- positive regulation of exosomal secretion
- peptidyl-aspartic acid autophosphorylation
- negative regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process
- cellular response to zinc ion
- calcium ion transmembrane transport
- regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process
- extracellular exosome biogenesis
- polyamine transmembrane transport
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001141973
NM_001141974
NM_022089 |
| NM_001164366
NM_029097
NM_001379619
NM_001379620
NM_001379621
|
|---|
NM_001379622 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001135445
NP_001135446
NP_071372
NP_001135445.1
NP_001135446.1 |
| NP_001157838
NP_083373
NP_001366548
NP_001366549
NP_001366550
|
|---|
NP_001366551 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 16.99 – 17.01 Mb | Chr 4: 140.71 – 140.73 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|















